 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Jan . 14, 2025 11:24
Back to list
types of pulley in belt conveyor
In the world of industrial and logistical operations, belt conveyors are ubiquitous. A crucial component of these systems is the pulley, playing a significant role in the efficiency and functionality of conveyor operations. Different types of pulleys are used depending on the specific requirements of the conveyor system. Understanding these variations not only enhances operational efficacy but also extends the lifespan of the machinery, ensuring maximal productivity and minimal downtime.
Specialized applications may also require wing pulleys, which have a unique spoke-like structure. These are typically used in environments where material buildup is a problem. The design of the winged pulley allows loose material to fall away rather than becoming trapped between the pulley and the belt, thereby reducing wear and maintaining belt cleanliness. Each type of pulley serves a distinct purpose and is optimized for specific operational conditions, underscoring the necessity for precise selection based on system needs. Choosing the right pulley configuration requires an understanding of the materials being transported, the environmental conditions, and the overall design of the conveyor system. An incorrect choice could lead to increased maintenance costs and unwanted interruptions in operations. From an operational standpoint, expertise and authority in pulley selection and maintenance are vital for industry professionals. Having a comprehensive understanding of pulley types not only improves the efficiency of the belt conveyor systems but also enhances trust among stakeholders. This trust translates into a perceived reliability that empowers businesses to operate seamlessly, reassured by machinery that is both competent and enduring. In conclusion, pulley selection is not merely a component choice but a strategic decision that impacts the entire conveyor system's operational excellence. Businesses seeking to optimize their logistical operations should focus on tailored pulley solutions, ensuring that the system's experience and reliability are uncompromised, ultimately enhancing their overall competitive advantage in the industry.
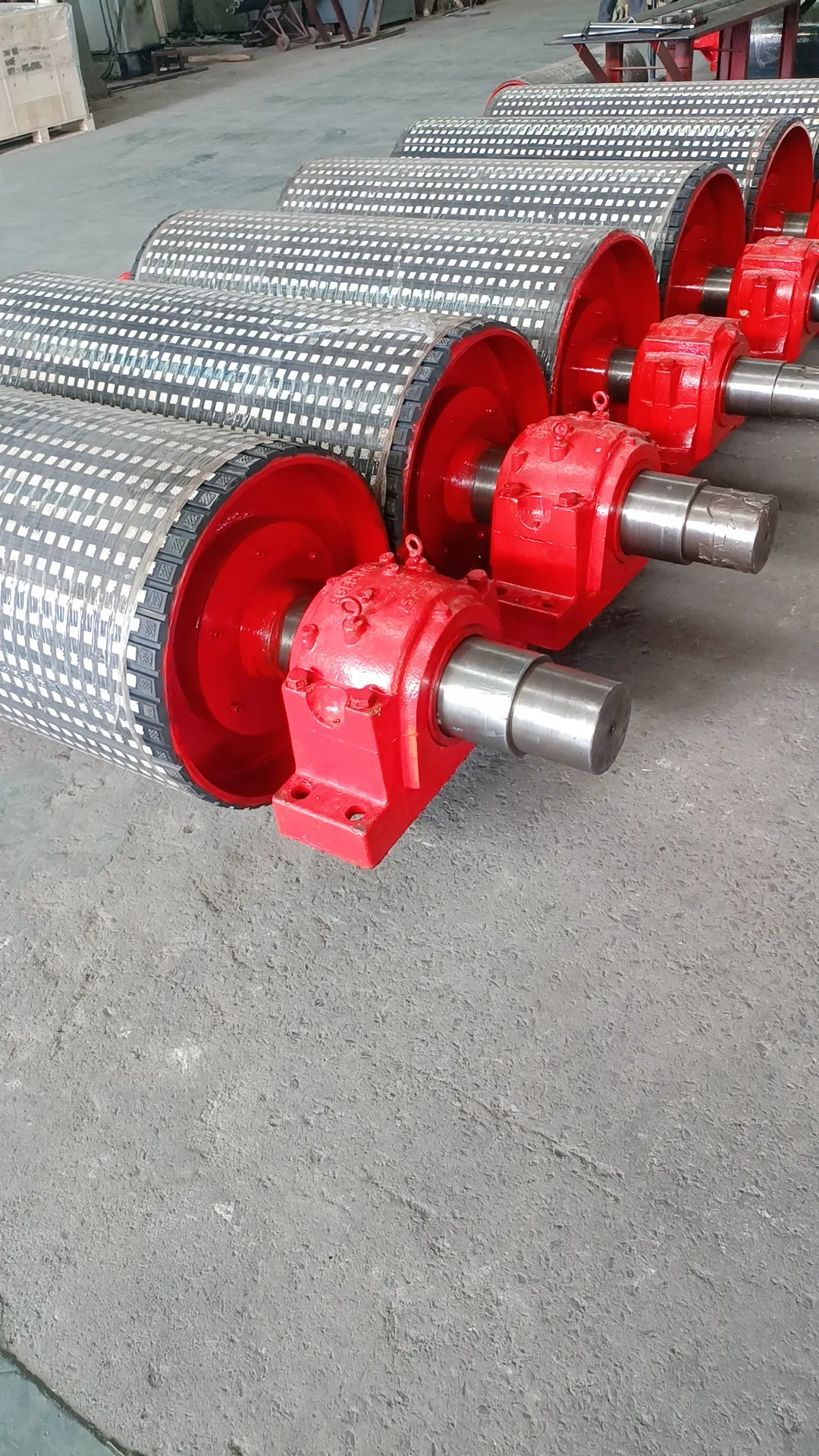
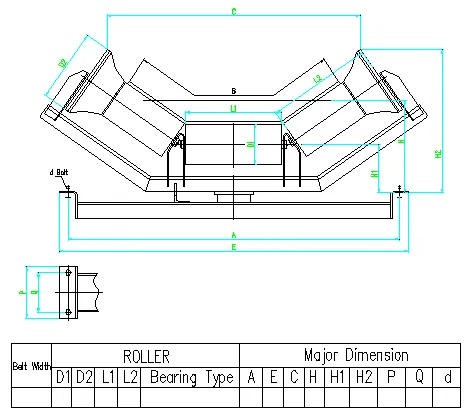

Specialized applications may also require wing pulleys, which have a unique spoke-like structure. These are typically used in environments where material buildup is a problem. The design of the winged pulley allows loose material to fall away rather than becoming trapped between the pulley and the belt, thereby reducing wear and maintaining belt cleanliness. Each type of pulley serves a distinct purpose and is optimized for specific operational conditions, underscoring the necessity for precise selection based on system needs. Choosing the right pulley configuration requires an understanding of the materials being transported, the environmental conditions, and the overall design of the conveyor system. An incorrect choice could lead to increased maintenance costs and unwanted interruptions in operations. From an operational standpoint, expertise and authority in pulley selection and maintenance are vital for industry professionals. Having a comprehensive understanding of pulley types not only improves the efficiency of the belt conveyor systems but also enhances trust among stakeholders. This trust translates into a perceived reliability that empowers businesses to operate seamlessly, reassured by machinery that is both competent and enduring. In conclusion, pulley selection is not merely a component choice but a strategic decision that impacts the entire conveyor system's operational excellence. Businesses seeking to optimize their logistical operations should focus on tailored pulley solutions, ensuring that the system's experience and reliability are uncompromised, ultimately enhancing their overall competitive advantage in the industry.
Next:
Latest news
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025
OUR PRODUCTS





























