 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Feb . 10, 2025 09:30
Back to list
types of conveyor pulley
In the ever-evolving world of industrial processes, the conveyor pulley holds a pivotal role in ensuring smooth and efficient operations. Among the various components of a conveyor system, pulleys are essential for directing and driving the belt. It’s crucial to understand the different types of conveyor pulleys to optimize system performance and reduce downtime. This guide delves into the distinct types, offering insights drawn from experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
Snub pulleys increase the belt’s arc of contact on the drive pulley to amplify friction and, consequently, the power transmitted from the motor to the belt. From decades of real-world application, it is understood that positioning snub pulleys close to the drive pulley’s arc prevents belt slippage and contributes to energy efficiency. These pulleys play a pivotal role in systems where space constraints require tighter pulleys arrangements while ensuring operational reliability. Take-up pulleys manage belt tension, crucial in maintaining non-slip drive conditions and prolonging belt life. In environments where temperature fluctuations could cause belt expansion or contraction, automatic tensioners have been embraced as a standard, ensuring consistent tension and improving reliability. Trustworthy reports from industries handling bulk materials emphasize the value of take-up systems in preventing operational outages and reducing maintenance frequency. Lastly, bend pulleys are employed to change the direction of the belt, providing flexibility in conveyor layouts. They are strategically placed to smoothen the directional transition while maintaining belt tension and alignment. The professionalism accumulated from various sectors suggests that employing rubber-coated bend pulleys can significantly reduce wear and tear, a testament to their utility in prolonging the belt’s operational lifespan. In conclusion, conveyor pulleys are indispensable to the efficacy of a conveyor belt system. Each pulley type serves a specific purpose that contributes to the seamless transportation of materials. With a blend of experience, cutting-edge expertise, authoritative standards, and steadfast reliability, understanding the intricacies of conveyor pulleys is instrumental in enhancing productivity and operational efficiency across different sectors. By investing in the correct pulley type and adhering to maintenance best practices, industries can optimize their conveyor systems to meet their precise needs, ultimately driving their operational success forward.
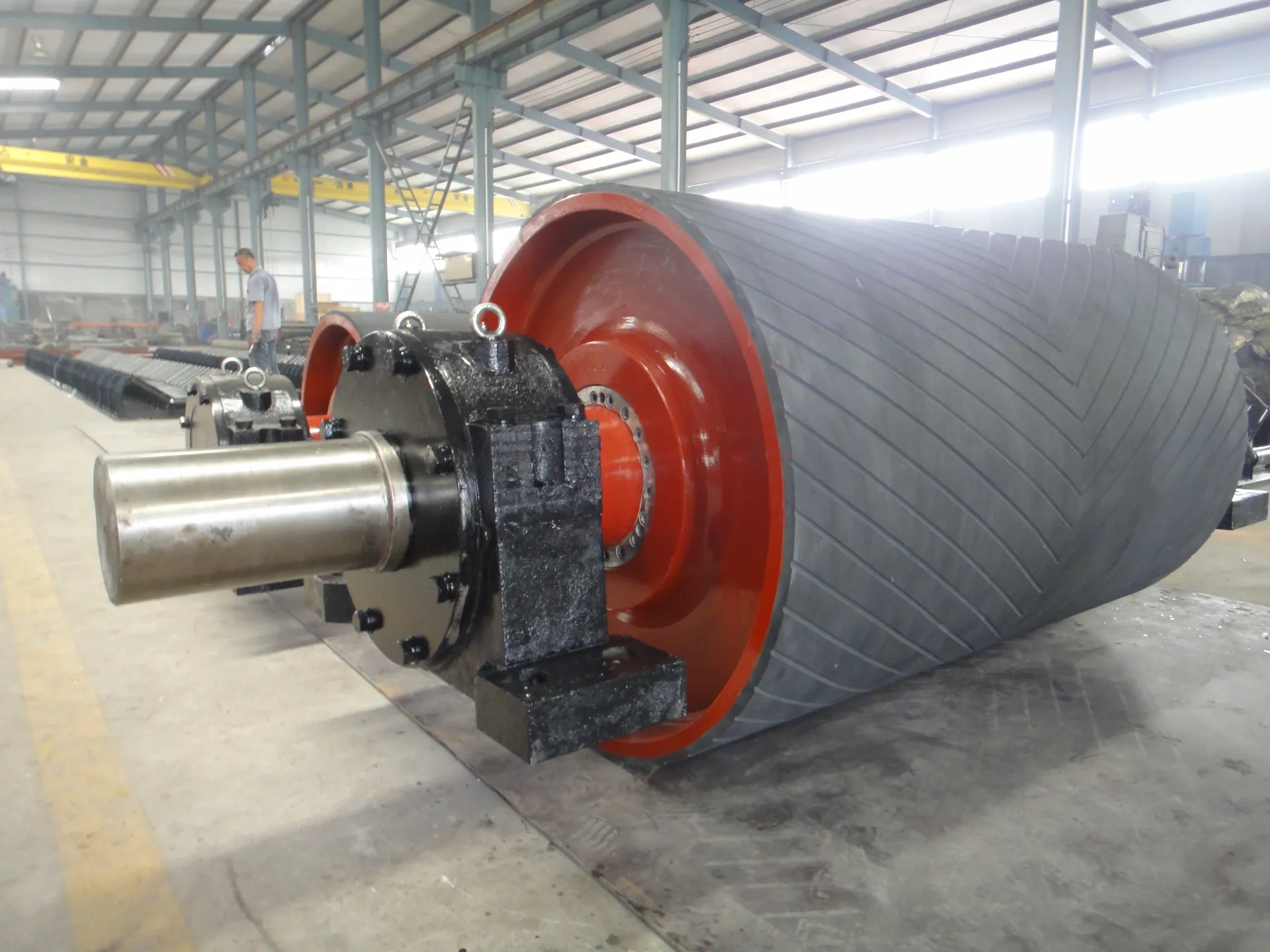

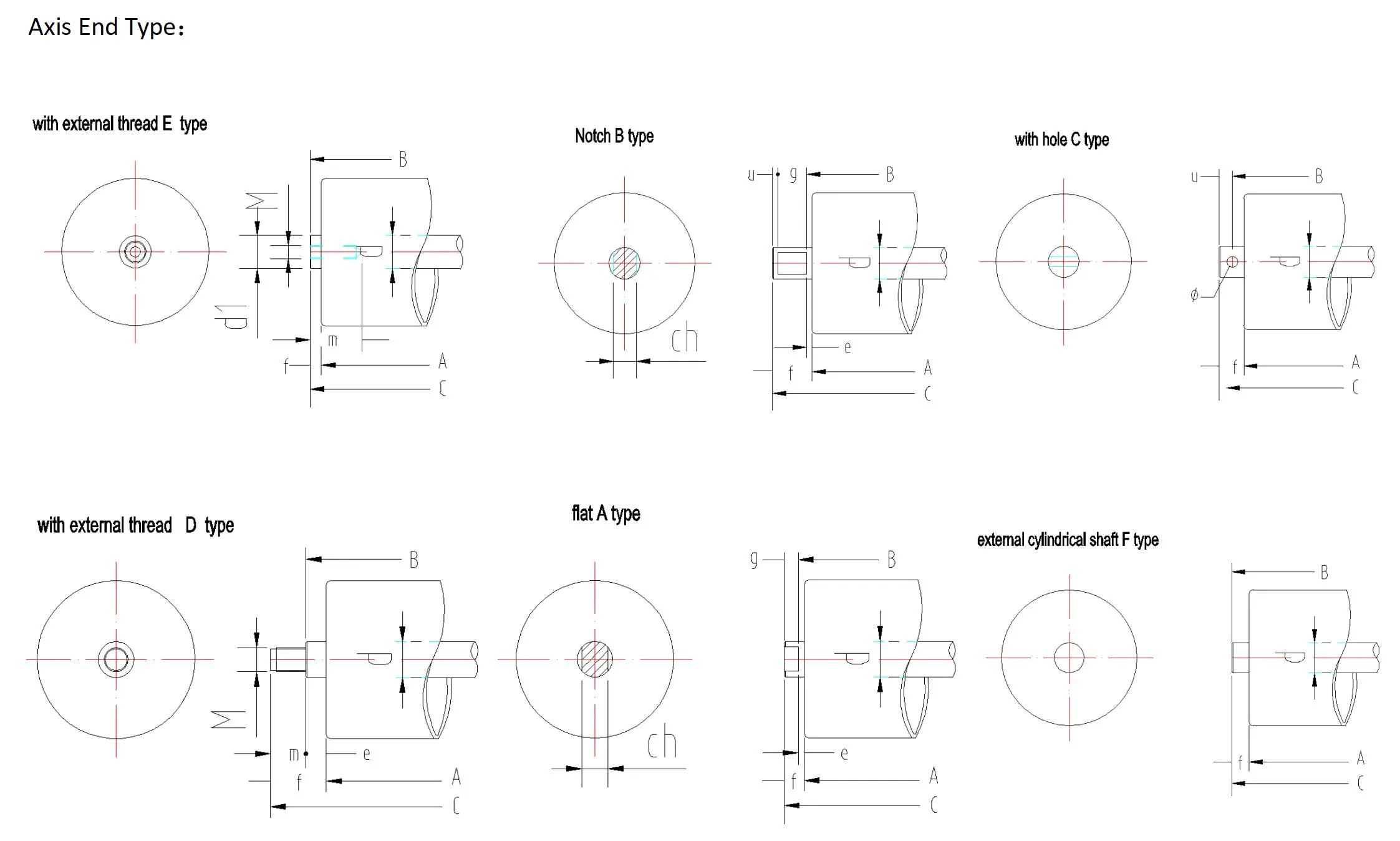
Snub pulleys increase the belt’s arc of contact on the drive pulley to amplify friction and, consequently, the power transmitted from the motor to the belt. From decades of real-world application, it is understood that positioning snub pulleys close to the drive pulley’s arc prevents belt slippage and contributes to energy efficiency. These pulleys play a pivotal role in systems where space constraints require tighter pulleys arrangements while ensuring operational reliability. Take-up pulleys manage belt tension, crucial in maintaining non-slip drive conditions and prolonging belt life. In environments where temperature fluctuations could cause belt expansion or contraction, automatic tensioners have been embraced as a standard, ensuring consistent tension and improving reliability. Trustworthy reports from industries handling bulk materials emphasize the value of take-up systems in preventing operational outages and reducing maintenance frequency. Lastly, bend pulleys are employed to change the direction of the belt, providing flexibility in conveyor layouts. They are strategically placed to smoothen the directional transition while maintaining belt tension and alignment. The professionalism accumulated from various sectors suggests that employing rubber-coated bend pulleys can significantly reduce wear and tear, a testament to their utility in prolonging the belt’s operational lifespan. In conclusion, conveyor pulleys are indispensable to the efficacy of a conveyor belt system. Each pulley type serves a specific purpose that contributes to the seamless transportation of materials. With a blend of experience, cutting-edge expertise, authoritative standards, and steadfast reliability, understanding the intricacies of conveyor pulleys is instrumental in enhancing productivity and operational efficiency across different sectors. By investing in the correct pulley type and adhering to maintenance best practices, industries can optimize their conveyor systems to meet their precise needs, ultimately driving their operational success forward.
Latest news
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025
OUR PRODUCTS





























