 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu drive belt idler
Understanding Drive Belt Idlers Their Importance and Functionality
Drive belt idlers are a crucial component in the mechanics of various machines, particularly in automotive and industrial applications. They play a significant role in ensuring smooth operation, efficient power transmission, and overall longevity of the belts they support. This article will delve into the nature of drive belt idlers, their functions, components, and maintenance, underscoring their importance in the broader scope of machinery and vehicle performance.
What is a Drive Belt Idler?
A drive belt idler is a pulley that guides or supports a drive belt within an engine or a machinery system. It is typically found in systems that utilize serpentine belts or V-belts. The idler pulley may not transmit power directly, but it helps maintain belt tension and proper alignment, which is essential for the effective operation of the belt-driven components.
Components of Drive Belt Idlers
Drive belt idlers generally consist of two main parts the pulley itself and the bearing that allows it to rotate smoothly. The pulley is usually made from durable materials such as steel or composite plastics to withstand wear and tear. The bearing can be either sealed or open, with sealed bearings typically offering better protection from dirt and debris, consequently increasing their lifespan.
Some idler pulleys also incorporate an adjustment mechanism that allows for the tension of the belt to be modified easily. This is crucial for maintenance and repair, as proper tension is vital for ensuring efficient operation and reducing the wear on both the belt and the idler.
Functions of Drive Belt Idlers
1. Tension Maintenance One of the primary functions of drive belt idlers is to maintain the appropriate tension in the belt. Insufficient tension can lead to belt slippage, reduced efficiency, and possible damage to both the belt and the driven components.
2. Belt Alignment Idlers help in aligning the belt properly within the system. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, noise, and potential failure of the system; therefore, idlers are positioned strategically to guide the belt.
drive belt idler
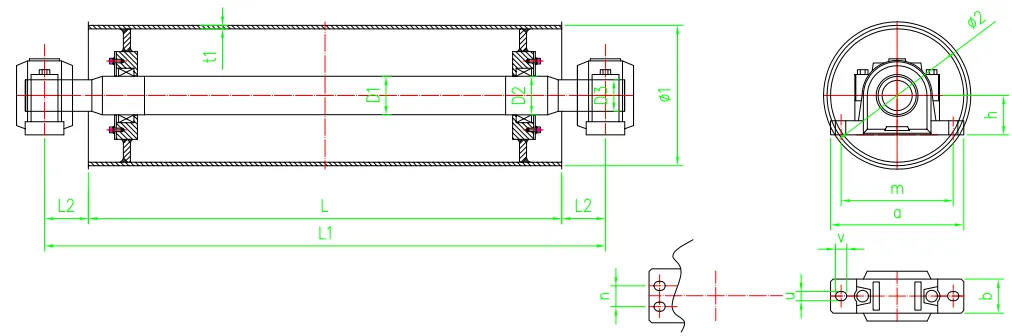
3. Reducing Vibration Drive belt idlers help alleviate some of the vibrations that may occur during operation. They provide a smoother path for the belt, ensuring quieter performance and reducing wear on associated components.
4. Supporting Other Components In some applications, the idler pulley may also serve a dual purpose, supporting other pulleys or components that are critical to the drivetrain's performance.
Maintenance of Drive Belt Idlers
Regular maintenance of drive belt idlers is essential for the longevity of both the idlers themselves and the belts they support. Here are some key maintenance tips
- Inspection Regularly inspect the condition of the idler pulley for any signs of wear, such as cracking, fraying, or misalignment. Early detection can prevent more severe issues down the line.
- Tension Checks Ensure that the belt tension is within the manufacturer's specifications. If the tension is too high or low, adjust it accordingly to prolong the life of both the belt and the idler.
- Lubrication Depending on the type of bearing used, it may be necessary to lubricate the idler pulleys periodically. Check manufacturers' guidelines regarding lubrication to avoid damaging the components.
- Replacement Idler pulleys will eventually wear out, and knowing when to replace them is critical. Signs that replacement is necessary include excessive noise, vibration, or visible damage.
Conclusion
Drive belt idlers are more than just passive components; they play an essential role in the functionality, efficiency, and reliability of machinery and vehicle systems. By understanding their functions, components, and maintenance needs, operators can ensure optimal performance and extend the life of drive belts and associated machinery. Regular checks and proper care of these components can prevent costly repairs and ensure smooth operations, making drive belt idlers a vital aspect of any mechanical system that relies on belt-driven technology.
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025





























