 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Conveyor Pulley Design Guidelines and Performance Specifications for Optimal Efficiency
Conveyor Pulley Specification An Essential Guide
Conveyor systems are indispensable in various industries, facilitating the movement of goods and materials efficiently. A fundamental component of these systems is the conveyor pulley, which plays a critical role in the functioning and reliability of the conveyor belt. Understanding the specifications of conveyor pulleys is paramount when designing, selecting, and maintaining conveyor systems to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Definition of Conveyor Pulleys
Conveyor pulleys are cylindrical devices that are used to support and drive the conveyor belt. They are typically located at the ends of the conveyor system, where they serve either to drive the belt (as head pulleys) or to return the belt (as tail pulleys). Additionally, there are other types of pulleys, such as bend pulleys and snub pulleys, which assist in changing the direction of the belt or increasing tension, respectively.
Key Specifications of Conveyor Pulleys
1. Diameter The diameter of the pulley is critical as it affects the belt's speed and the overall performance of the conveyor system. Common diameters range from 4 inches to 24 inches, depending on the application and the load handling requirements. Larger pulleys can accommodate heavier loads and reduce belt wear.
2. Material Conveyor pulleys are typically made from various materials, including steel, aluminum, and plastic. Steel pulleys are the most common due to their strength and durability. The choice of material may depend on factors such as the environment (e.g., corrosive conditions), weight restrictions, and budget.
3. Construction Type Pulleys can be constructed as solid or hollow cylinders. Solid pulleys are often used for heavy-duty applications, while hollow pulleys are lighter and may be used in applications where weight savings are essential.
conveyor pulley specification
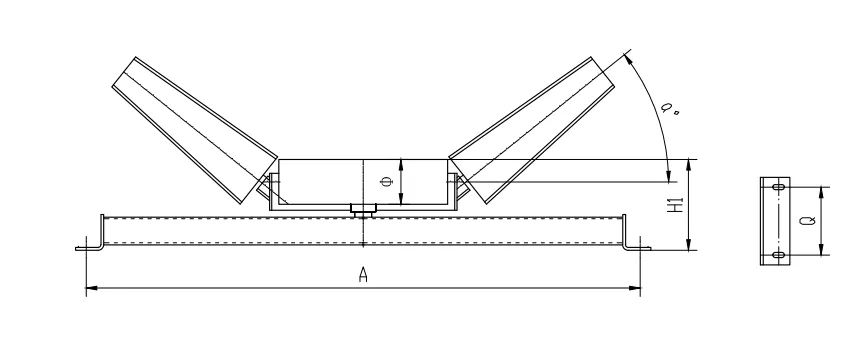
4. Shaft Size and Type The shaft supports the pulley and connects it to the drive mechanism. The shaft size must be sufficient to handle the loads and stresses encountered during operation. Standard shaft types include keyed, splined, or plain, and the selection depends on the method of connection to the drive.
5. Bushing Type Pulleys may employ different bushing types, which determine how the pulley is mounted on the shaft. Options include fixed, adjustable, or split bushings, each having implications on maintenance and ease of replacement.
6. Crowning The crown on a pulley refers to its slightly raised center, which helps keep the conveyor belt aligned and prevents it from drifting off. The crowning specification is essential, particularly in high-speed applications, where belt tracking can be critical.
7. Load Capacity Understanding the load capacity of the pulley is vital for ensuring it can withstand the operational pressures without failure. Manufacturers often provide load rating guidelines based on different factors, including the type of material being transported, speed, and environmental conditions.
8. Finish and Coating The surface finish or coating of a pulley can significantly impact its resistance to wear and environmental effects. Common finishes include galvanized, painted, or coated options, which help extend the life of the pulley in various industrial conditions.
Conclusion
Selecting the right conveyor pulley for a specific application entails a comprehensive understanding of these key specifications. Engineers and procurement specialists must consider the load requirements, environmental conditions, and the desired longevity of the conveyor system while making their choice. By adhering to proper specifications and maintenance procedures, facilities can enhance operational efficiency, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of their conveyors — ultimately leading to improved productivity and reduced operational costs.
As conveyor systems continue to evolve with advancements in technology and increased operational demands, attention to pulley specifications will remain crucial in supporting effective material handling solutions across diverse industries.
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025





























