 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Conveyor System Components Including Head and Tail Pulleys for Efficient Material Handling
Conveyor Head and Tail Pulley A Key Component in Material Handling Systems
In industrial applications, conveyors play a pivotal role in facilitating the movement of materials across various processes. At the heart of any conveyor system are the head and tail pulleys, which are essential components that ensure the efficient operation of the conveyor belt. Understanding their function and significance is crucial for anyone involved in material handling or conveyor system design.
The head pulley, located at the discharge end of the conveyor, is the driving force that propels the belt forward. It is typically powered by a motor, which is connected through a series of gears and pulleys. The head pulley exerts tension on the conveyor belt, allowing it to transport materials smoothly and consistently. Its rotating motion creates friction against the belt, facilitating movement while also helping to maintain proper alignment and tracking.
Conveyor Head and Tail Pulley A Key Component in Material Handling Systems
Both pulleys are typically made from durable materials such as steel or cast iron, allowing them to withstand significant wear and tear during operation. The design of these pulleys often includes features such as lagging—a rubber or composite layer on the pulley surface that enhances grip and minimizes slippage. This is particularly important in applications where the conveyed materials may be heavy or abrasive, as it extends the life of the conveyor belt and improves overall efficiency.
conveyor head and tail pulley
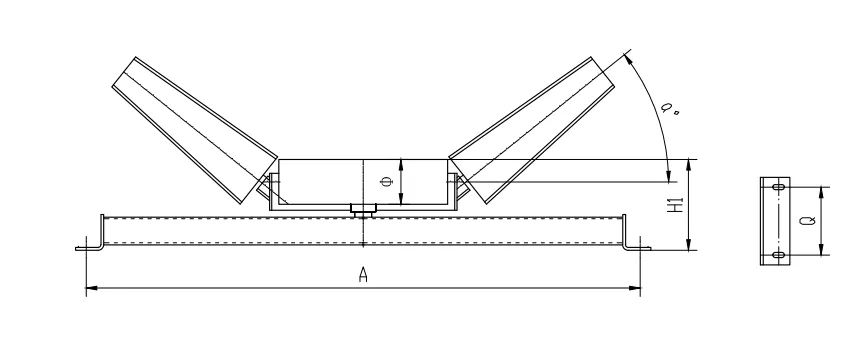
Regular maintenance of head and tail pulleys is essential to ensure optimal performance. This includes checking for signs of wear on the pulley surfaces, ensuring that the motors and drives are functioning correctly, and verifying that the belt is properly aligned. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear on the belt, increasing the likelihood of breakdowns and reducing the lifespan of both the belt and the pulleys.
In addition to maintenance, the selection of the appropriate head and tail pulley for a conveyor system is crucial. Factors such as the weight of the materials being conveyed, the speed of the conveyor, and the environmental conditions must all be considered. For example, in heavy-duty applications, a larger diameter head pulley may be needed to provide sufficient torque and prevent slippage, while in environments with high humidity, corrosion-resistant materials may be required to ensure durability.
The innovations in conveyor technology have also impacted the design and functionality of head and tail pulleys. Advances such as variable speed drives enable more control over the belt speed, which can optimize material handling processes. Furthermore, the integration of sensors and smart technology allows for real-time monitoring of conveyor performance, identifying issues before they result in costly downtime.
In conclusion, the head and tail pulleys are integral components of conveyor systems that significantly influence their efficiency and reliability. Understanding their roles, maintaining best practices, and keeping abreast of technological advancements play essential roles in maximizing productivity in material handling operations. Whether in mining, manufacturing, or logistics, the effectiveness of conveyor systems relies heavily on these vital components. Proper attention to the design, selection, and maintenance of head and tail pulleys can lead to improved operational performance and reduced costs over time.
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025





























