 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu belt conveyor idler design
Belt Conveyor Idler Design An Overview
Belt conveyors are integral components of material handling systems across various industries, including mining, manufacturing, and logistics. One of the critical elements in the design and efficiency of belt conveyors is the idler. The idler, which supports the belt, plays a crucial role in ensuring that the conveyor system operates effectively and efficiently. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of belt conveyor idler design, including types, materials, load capacities, and maintenance considerations.
Types of Idlers
Belt conveyor idlers can be classified into several categories based on their design and application. The main types include
1. Carrying Idlers These idlers support the weight of the conveyed materials. Carrying idlers can further be categorized into troughing idlers, flat idlers, and transition idlers. Troughing idlers are the most common, with a curved design that allows for better containment of bulk materials.
2. Return Idlers Positioned on the return side of the conveyor, return idlers support the empty belt as it returns to the loading point. They help maintain proper belt tension and alignment.
3. Impact Idlers These are specially designed to absorb the shock of heavy bulk materials falling onto the conveyor. Impact idlers typically feature a robust construction to withstand significant forces.
4. Training Idlers These idlers are used to control the alignment of the conveyor belt. They help prevent belt mistracking and ensure that the belt runs straight along the conveyor path.
Materials and Construction
The materials used in idler construction significantly impact their performance, durability, and maintenance needs. Common materials include
- Steel Often used for heavy-duty application idlers due to its strength and ability to withstand harsh environments. Steel idlers are typically coated with anti-corrosive materials to extend their lifespan.
- Plastic Lightweight and resistant to moisture, plastic idlers are suitable for environments where corrosion is a concern. However, they may not be ideal for extremely heavy loads.
belt conveyor idler design
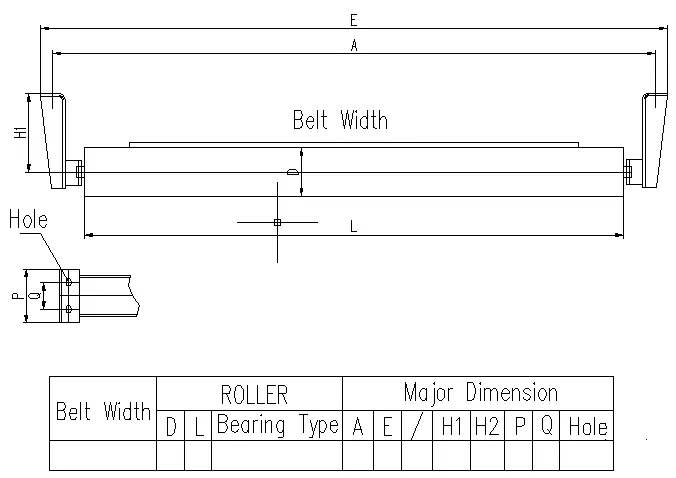
- Rubber Used primarily for impact idlers, rubber provides excellent shock absorption and can reduce belt wear.
The design of the idler also includes considerations for the size and weight. Idlers must be optimized for the specific loads they will carry, taking into account factors such as belt width, material type, and operating conditions.
Load Capacity and Performance
One of the critical parameters in idler design is the load capacity. This is defined by the amount of weight that an idler can support without deforming or failing. Engineers calculate load capacities by considering factors such as belt tension, angle of repose of the bulk material, and environmental conditions (like temperature and humidity).
Performance metrics, including frictional resistance and belt sag, are also considered during the design phase. A well-designed idler will minimize frictional losses, enhance material flow, and reduce wear on both the idler itself and the conveyor belt.
Maintenance Considerations
Regular maintenance of idlers is crucial to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the entire conveyor system. Common maintenance practices include
- Inspection Periodic inspections can identify potential issues before they lead to failures. Key areas to inspect include roller rotation, alignment, and wear on the bearings.
- Lubrication Adequate lubrication of the bearings reduces friction and wear, extending the life of the idlers.
- Replacement Identifying when an idler has reached the end of its operational life is crucial. Signs of excessive wear or damage should prompt immediate replacement to prevent disruptions in the conveyor system.
Conclusion
In summary, the design of belt conveyor idlers is a multi-faceted process that plays a critical role in the overall performance and reliability of conveyor systems. Through careful consideration of types, materials, load capacities, and maintenance practices, engineers can create idler systems that support efficient material handling operations. By investing in quality idler design and maintenance, companies can reduce downtime, enhance productivity, and ultimately achieve more reliable supply chain operations. As technology advances, continued innovation in idler design will further improve the efficiency of belt conveyors across various industries.
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025





























