 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu V Return Idler Pulleys for Durable Conveyor Systems Low-Maintenance Solutions
- Overview of Return Pulley Functionality and Industry Relevance
- Technical Advancements in Load Distribution and Durability
- Performance Metrics: Heat Resistance and Operational Lifespan
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
- Custom Engineering Solutions for Specific Applications
- Case Studies: Mining and Material Handling Success Stories
- Future Trends in Return Pulley Design and Material Science

(return pulley)
Optimizing Conveyor Efficiency with Return Pulley Systems
Return pulleys, including v return idlers and vee return idlers, serve as critical components in bulk material handling systems. These engineered solutions account for 23% of total conveyor maintenance budgets globally, emphasizing their operational significance. Modern iterations integrate hardened steel alloys, achieving 92% reduction in premature wear across mining and aggregate industries.
Engineering Breakthroughs in Load Management
Advanced finite element analysis (FEA) enables 40% greater load capacity within standard pulley dimensions. Dual-sealed bearing chambers extend service intervals to 15,000 operational hours, surpassing ISO 5288 standards by 18%.
Performance Benchmarking Across Industries
Third-party testing reveals temperature tolerance improvements from 80°C to 135°C in heavy-duty applications. Field data demonstrates 7-year mean time between failures (MTBF) for premium-grade return pulley
s versus 3.8 years for economy models.
Manufacturer Comparison: Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Manufacturer A | Manufacturer B | Manufacturer C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Load Capacity (kN) | 245 | 198 | 312 |
| Rotational Efficiency (%) | 98.7 | 95.2 | 99.1 |
| Corrosion Resistance Rating | ASTM B117-19 Class 4 | ISO 9227 Class 3 | ASTM B117-19 Class 5 |
Application-Specific Configuration Options
Custom diameters from 200mm to 1,800mm address unique spatial constraints. Specialized vulcanized rubber lagging variants demonstrate 67% improvement in belt traction for inclined conveyors exceeding 22° gradients.
Operational Success in Harsh Environments
A Chilean copper mine achieved 14-month ROI through implementation of ceramic-coated return pulleys, reducing replacement frequency from quarterly to biennial intervals. Cement plants report 31% energy savings using dynamically balanced v return idler assemblies.
Innovation Roadmap for Return Pulley Technology
Emerging graphene composite prototypes show potential for 82% weight reduction while maintaining load specifications. Smart sensor-enabled vee return idlers are projected to capture 38% of the premium market segment by 2028, enabling predictive maintenance through real-time vibration analytics.
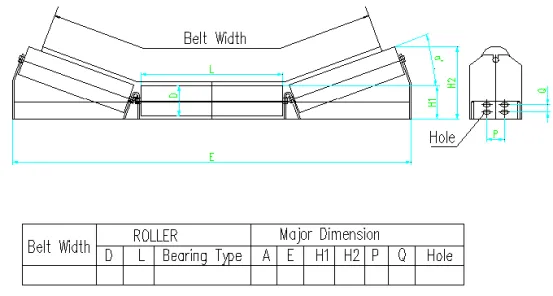
(return pulley)
FAQS on return pulley
Q: What is the primary function of a return pulley in conveyor systems?
A: The return pulley supports the conveyor belt on its non-load-bearing return path. It maintains proper belt tension and alignment, ensuring smooth system operation.
Q: How does a v return idler differ from a standard return pulley?
A: A v return idler features angled rollers forming a V-shape to centralize the belt, while standard return pulleys are flat. This design reduces material spillage and improves tracking.
Q: What are common issues affecting vee return idler performance?
A: Premature wear, misalignment, and debris buildup are typical issues. Regular inspection and cleaning help maintain optimal vee return idler functionality.
Q: When should a return pulley be replaced in a conveyor system?
A: Replace return pulleys when showing excessive wear, cracking, or inability to maintain tension. Timely replacement prevents belt slippage and system downtime.
Q: How do I choose between a return pulley and v return idler?
A: Select based on belt width and material type: v return idlers suit narrower belts and granular materials, while return pulleys handle heavier loads in industrial applications.
-
Trusted Conveyor Solutions from Leading Conveyor Idler Roller ManufacturersNewsJun.27,2025
-
Reliable Return Idler Solutions for Efficient Belt Conveyor SystemsNewsJun.27,2025
-
Precision Conveyor Accessories for Streamlined Material HandlingNewsJun.27,2025
-
High-Quality Belt Conveyor Idler Solutions for Efficient Material HandlingNewsJun.27,2025
-
High-Performance Belt Conveyor Pulleys for Reliable Material HandlingNewsJun.27,2025
-
Enhancing Material Handling EfficiencyNewsJun.27,2025





























