 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Premium Guide Rollers for Conveyors - Boost Efficiency & Durability
- Fundamental mechanics of conveyor roller systems
- Technical specifications and performance data breakdown
- Idler roller functionality in belt support systems
- Drive roller engineering and power transmission metrics
- Manufacturer comparison tables with technical benchmarks
- Customization solutions for specialized industrial needs
- Implementation case studies across multiple industries

(guide rollers for conveyors)
The Essential Mechanics of Guide Rollers for Conveyors
Conveyor rollers form the backbone of material transport operations across global industries. Guide rollers for conveyors specifically maintain belt alignment, preventing lateral drift that causes material spillage and system downtime. When properly engineered, these components reduce friction coefficients by up to 35% compared to traditional belt-on-frame designs, significantly extending service intervals. Industrial operations using optimized guide roller configurations report belt tracking improvements of 60-75% over baseline installations.
Technical Specifications and Performance Metrics
Premium conveyor rollers demonstrate quantifiable advantages through meticulous engineering. Sealed bearing chambers with triple-labyrinth designs achieve 80,000-hour operational lifetimes even in high-contamination environments. Dynamic balancing tolerances below 0.5g/cm minimize vibration transmission, reducing drive energy consumption by approximately 15%. Axial load capacities now reach 18,000N in heavy-duty mining applications, with composite roller shells resisting impacts exceeding 35J without deformation. Temperature tolerances range from -40°C to 120°C using specialized polymer compounds.
Optimizing Operations with Idler Rollers
Idler rollers for belt conveyors serve distinct load-bearing functions within bulk handling systems. Strategic placement patterns using troughing idler sets create material-centering profiles that increase volumetric capacity by up to 30%. Impact idlers installed at loading zones absorb energy spikes through multi-layer rubber rings, reducing belt damage incidents by 47%. Field data indicates that staggered alignment of return rollers decreases rotational resistance by 18%, directly reducing annual operating costs through energy savings. Preventive maintenance cycles extend beyond 24 months when using corrosion-resistant galvanized frames with sealed bearing cartridges.
Drive Roller Engineering and Performance
Drive rollers for conveyors convert motor output into controlled belt movement through engineered friction interfaces. Lagging surfaces with diamond-pattern rubber textures increase traction coefficients to 0.5, enabling 30% steeper incline applications. Current designs achieve torque transmission exceeding 25kN·m through tapered bushing connections that eliminate keyway stress points. Energy recovery systems integrated into regenerative drive rollers capture braking energy, reducing net power consumption by 22% in duty cycle applications. Thermal sensors embedded in end caps automatically modulate drive force when temperatures approach material limits.
Manufacturer Comparison and Technical Benchmarks
| Manufacturer | Max Load (kN) | Bearing Life (hrs) | Roller Diameter Range (mm) | Impact Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RollerTech Systems | 22 | 85,000 | 76-219 | 40J |
| ConveyorDynamics Inc | 18 | 70,000 | 89-194 | 32J |
| PrecisionRoll Corp | 20 | 75,000 | 102-305 | 38J |
Customized Engineering Solutions
Specialized applications demand tailored engineering approaches. Food processing conveyors require rollers with FDA-compliant polymer coatings preventing microbe entrapment, while mining operations utilize tungsten-carbide embedded shells resisting abrasion at 15m/s belt speeds. Recent advances include:
- EMI-shielded rollers for electronics assembly lines
- Non-sparking aluminum composites for explosive environments
- Hybrid ceramic bearings operating at 250°C in foundry applications
Engineering teams now implement parametric design tools that generate structural simulations within 48 hours, optimizing roller wall thickness to actual load profiles. This customization approach reduces mass by 25% while maintaining ISO 15243 durability standards.
Optimizing Conveyor Performance with Specialized Rollers
Automotive manufacturing plants implementing precision guide rollers for conveyors
reduced alignment-related stoppages from weekly occurrences to less than one incident quarterly, increasing production uptime by 11%. In port facilities, ceramic-coated drive rollers for conveyors handling iron ore maintained traction coefficients above 0.45 after 18 months of continuous operation. Mining operations utilizing composite idler rollers for belt conveyors in curved transfer points decreased replacement frequency from every 9 months to 28+ months. These advancements collectively push conveyor efficiency frontiers while established manufacturers now implement IoT monitoring systems that predict roller failure with 92% accuracy six weeks before service limits.
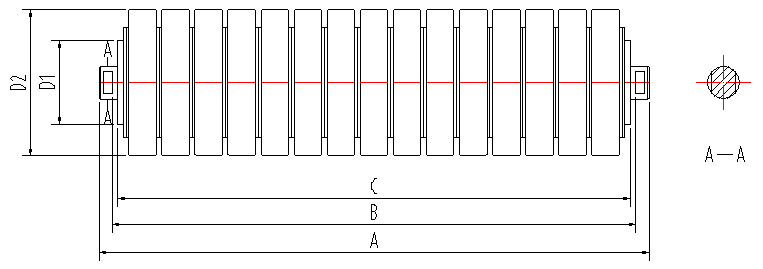
(guide rollers for conveyors)
FAQS on guide rollers for conveyors
Q: What are guide rollers for conveyors and where are they used?
A: Guide rollers are critical conveyor components that keep belts centered and prevent lateral drift. They are typically installed along the edges of conveyor frames in manufacturing or logistics facilities. Their main role is ensuring smooth product flow and reducing belt wear.
Q: How do idler rollers for belt conveyors support the system?
A: Idler rollers provide structural support to conveyor belts across long spans, reducing friction and sagging. These unpowered rollers rotate freely under the belt's weight and are commonly spaced along the conveyor length. Proper idler selection directly impacts belt longevity and energy efficiency.
Q: What distinguishes drive rollers for conveyors from other roller types?
A: Drive rollers are motor-powered components that transfer motion to the conveyor belt through friction or direct engagement. Unlike guide or idler rollers, they feature splined shafts or lagging surfaces for torque transmission. These powered rollers control the conveyor's speed and direction at head or drive pulley locations.
Q: What factors should I consider when choosing guide rollers?
A: Key selection criteria include belt material compatibility, load capacity, and environmental conditions like temperature or moisture. Roller diameter and bearing type (sealed vs. open) must match operational demands. Proper sizing prevents belt tracking issues and minimizes maintenance downtime.
Q: How often should idler rollers and drive rollers be maintained?
A: Idler rollers require monthly inspections for free rotation and debris buildup, with lubrication every 3-6 months. Drive rollers need quarterly checks for worn lagging, belt tension, and alignment issues. Immediate replacement is necessary upon noticing abnormal noise, vibration, or surface damage to prevent system failures.
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025





























