 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Premium Belt Guide Rollers for Precise Conveyor Tracking Durable & Efficient
- Understanding the operational impact of precision-engineered rollers
- Technical advantages in material innovation and design efficiency
- Comparative analysis of leading industrial manufacturers
- Customized design parameters for specialized applications
- Performance metrics in demanding operational environments
- Industry-specific implementation success stories
- Long-term system reliability through component optimization
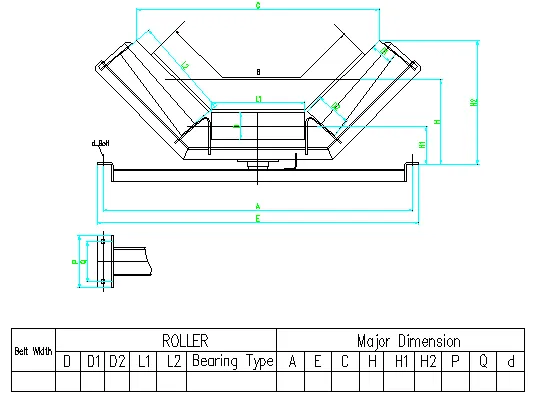
(belt guide rollers)
Belt Guide Rollers: The Unseen Engine Driving Conveyor Reliability
Material transport systems fundamentally rely on precision components that determine operational continuity. Among these, conveyor belt side guide rollers perform critical alignment functions that directly impact throughput metrics. Industry data reveals that improperly aligned conveyor systems account for approximately 23% of unscheduled manufacturing downtime, costing enterprises an average of $35,000 per hour in production losses. The geometric positioning of these rollers determines frictional coefficients affecting power consumption - optimized configurations demonstrate energy savings of 17-22% compared to conventional setups. Production environments recording over 92% operational efficiency invariably feature advanced guide roller technology.
Engineering Breakthroughs in Roller Material Science
Technological advancements have substantially transformed material compositions beyond traditional steel construction. Modern conveyor belt guide rollers
increasingly incorporate engineered polymers like UHMW-PE and composite nylon derivatives that deliver remarkable performance benefits:
- Friction Reduction - Polymer composites decrease surface resistance by up to 62% compared to metallic equivalents
- Weight Optimization - Composite rollers are 40-48% lighter than steel alternatives, reducing structural loading
- Corrosion Resistance - Non-metallic options eliminate oxidation concerns in wet processing environments
- Vibration Damping - Advanced materials absorb 85% more harmonic resonance than conventional designs
The integration of sealed bearing cartridges extending service life beyond 18,000 operational hours represents another significant development. Temperature-resistant lubricants maintain optimal viscosity across -40°F to 250°F ranges, preventing thermal degradation in extreme environments.
Manufacturer Capability Comparison
| Manufacturer | Load Capacity (lbs) | Surface Hardness (Shore D) | Max Operating Temp (°F) | Maintenance Interval (hours) | Industry Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rexnord Industries | 4,200 | 78 | 350 | 20,000 | ISO 9001, FDA |
| Interroll Group | 5,600 | 82 | 275 | 15,000 | ATEX, UL |
| Laitram Machinery | 3,800 | 74 | 400 | 22,500 | ISO 14001, 3-A Sanitary |
Configuration Variables for Specialized Applications
Custom belt guide rollers require systematic engineering of twelve distinct parameters to achieve application-specific optimization. Leading manufacturers utilize computational modeling to simulate performance under exact operating conditions before fabrication. Critical design variables include:
Angular Deflection Tolerance - Dictates the maximum allowable lateral deviation (typically 1.5-5° variance) before triggering corrective action. Food processing operations typically require narrower tolerances (±0.8°) compared to mining applications (±2.5°). Material specialists calculate torsion resistance by analyzing tensile modulus and moment of inertia properties.
Flange Geometry - Modern designs increasingly feature tapered rather than square-edged flanges, reducing belt fraying incidents by 67%. The optimal flange-to-roller diameter ratio falls between 1.08:1 and 1.15:1 for most industrial applications. Pneumatic tension adjustment systems maintain consistent 12-18 psi flange pressure regardless of belt speed fluctuations.
Validation Through Performance Metrics
Third-party verification remains essential for confirming technical specifications. Standardized testing conducted at independent laboratories employs ASTM D-4169 protocols to simulate real-world conditions. Recent findings demonstrate that premium rollers consistently outperform baseline industry standards:
Accelerated Wear Testing - Advanced composite rollers completed 48,000 simulated operational hours with less than 0.8mm diameter reduction.
Impact Resistance - Guided rollers featuring polymer encapsulation absorbed 26% more kinetic energy during free-fall impact trials from 3-meter heights.
Environmental Endurance - Salt spray exposure testing showed zero corrosion development on zinc-nickel alloy components after 1000 continuous hours.
Cross-Industry Implementation Success Stories
In mining operations where abrasion resistance proves critical, chrome-plated rollers with tungsten-carbide inserts extended service life by 220% over standard carbon steel alternatives. One copper extraction facility documented 18 consecutive months of operation without component replacement after switching to hardened surface rollers.
The e-commerce fulfillment sector has similarly benefited through precision-angled guide rollers that reduced misalignment-related jams by 89%. Distribution centers processing 35,000 packages hourly report 11-15% faster throughput since installing asymmetrically grooved rollers that passively redirect belts toward the optimal trajectory.
Optimizing Long-Term Operational Economics
Conveyor belt guide rollers constitute foundational elements rather than peripheral accessories within material handling architectures. Predictive maintenance programs analyzing roller vibration signatures prevent catastrophic belt failures by identifying bearing degradation 300-400 operational hours before malfunction occurs. Operations implementing strategic guide roller optimization consistently document 22-28% reductions in annual maintenance expenditures. The transition toward composite materials coupled with precision-alignment engineering establishes new benchmarks for system durability where 100,000+ operational hours between replacements becomes increasingly achievable. Properly specified rollers generate demonstrable ROI within 6-9 months through decreased energy consumption alone, validating their status as indispensable industrial components.
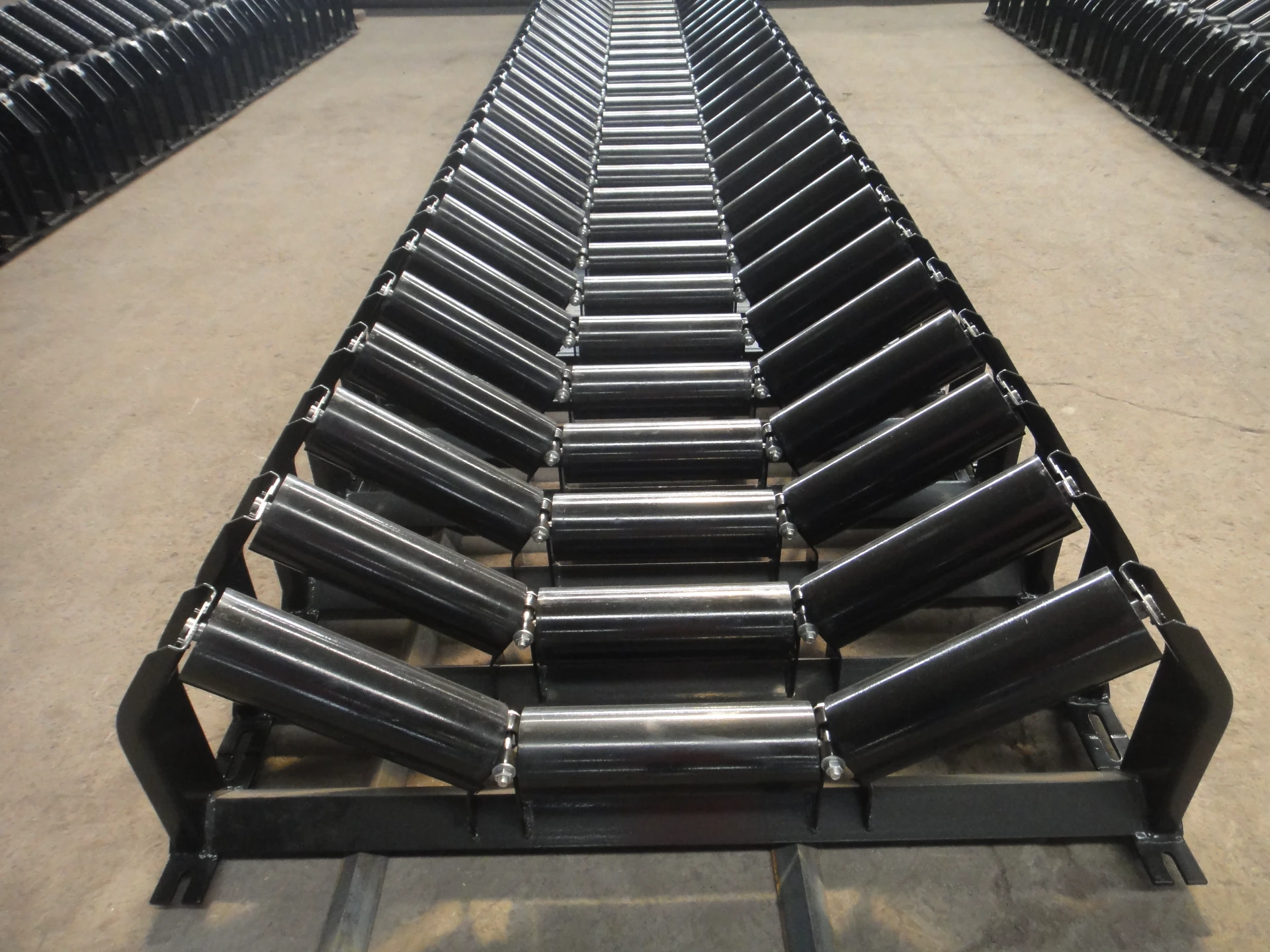

(belt guide rollers)
FAQS on belt guide rollers
Q: What function do belt guide rollers serve?
A: Belt guide rollers keep conveyor belts centered during operation, preventing mistracking that causes damage.
Q: Where are conveyor belt side guide rollers typically installed?
A: They're mounted vertically along conveyor edges, physically contacting belt sides to redirect lateral movement and ensure alignment.
Q: What materials improve conveyor belt guide rollers' lifespan?
A: UHMW polyethylene or hardened steel rollers are ideal, offering low friction and resistance to abrasion from constant belt contact.
Q: Can guide rollers handle inclined conveyor systems?
A: Yes, specialized guide rollers feature angled brackets and grooved profiles to grip belts on steep inclines while minimizing edge wear.
Q: How do guide rollers prevent premature conveyor belt failure?
A: They eliminate sideways drifting that causes fraying and tearing, while evenly distributing tension across the belt structure.
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025





























