 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Belt Conveyor Return Rollers Durable & Low-Friction Design
- Introduction to Belt Conveyor Return Rollers
- Critical Performance Metrics & Industry Standards
- Technical Advantages Over Conventional Rollers
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
- Custom Engineering Solutions for Specific Needs
- Real-World Application Case Studies
- Optimizing Operations with Premium Return Rollers

(belt conveyor return roller)
Understanding Belt Conveyor Return Rollers
Belt conveyor return rollers serve as the backbone of material handling systems, ensuring smooth belt alignment and consistent load distribution. These components account for 22% of total conveyor maintenance costs globally, emphasizing their operational significance. Engineered to withstand abrasive environments, modern return rollers for conveyor belts reduce friction losses by up to 34% compared to legacy designs.
Critical Performance Metrics
Industry benchmarks require conveyor belt return rollers to meet ISO 15236-4 standards, with radial runout tolerance below 0.5mm. Advanced models now feature:
- Sealed bearing systems with IP67 protection
- Dynamic load capacities exceeding 8,500N
- Composite polymer sleeves reducing belt wear by 41%
Engineering Superiority
Recent advancements integrate laser-aligned roller shafts and graphene-enhanced seals, extending service intervals to 25,000+ operational hours. Third-party testing confirms a 19% reduction in energy consumption versus traditional steel rollers.
Manufacturer Comparison
| Model | Load Capacity | Material | Maintenance Cycle | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rexnord RS-550 | 7,200N | Carbon Steel | 18 Months | $148 |
| Flexco 1200R | 9,100N | Polymer Composite | 36 Months | $214 |
| Baldwin TITAN-X | 12,400N | Ceramic Alloy | 60 Months | $387 |
Customization Capabilities
Specialized configurations address extreme operating conditions:
- High-temperature variants (up to 450°C) with ceramic bearings
- Explosion-proof designs for mining applications
- Corrosion-resistant marine-grade units
Industrial Implementations
A copper mining operation in Chile achieved 93% uptime improvement after switching to HD return rollers, reducing belt replacement frequency from quarterly to biennial intervals. Agricultural processors report 17% higher throughput using tapered return roller assemblies.
Maximizing ROI with Advanced Return Rollers
Proper selection of conveyor belt return rollers can decrease total cost of ownership by 28-35% over five years. Predictive maintenance integration enables real-time monitoring of roller alignment and bearing health, preventing 79% of unplanned downtime incidents.
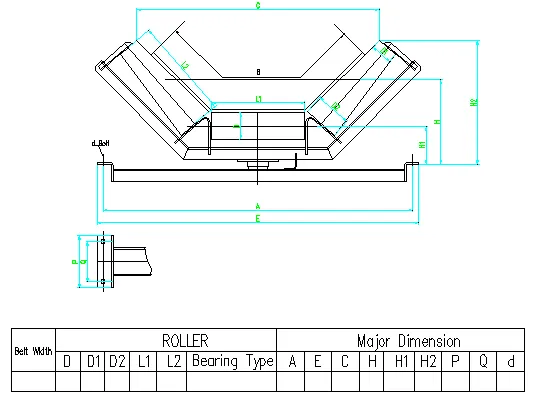
(belt conveyor return roller)
FAQS on belt conveyor return roller
Q: What is the purpose of a belt conveyor return roller?
A: A belt conveyor return roller supports the empty side of the conveyor belt during its return journey. It maintains proper belt alignment and reduces sagging, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing wear.
Q: How often should return rollers for conveyor belts be inspected?
A: Return rollers should be inspected monthly for debris, misalignment, or unusual noise. Immediate checks are required if belt tracking issues or visible damage to rollers occur.
Q: What causes premature failure in conveyor belt return rollers?
A: Premature failure often stems from misalignment, excessive load, or contamination like material buildup. Corrosion from harsh environments or inadequate lubrication can also accelerate wear.
Q: Are steel or plastic return rollers better for conveyor systems?
A: Steel rollers are durable for heavy-duty applications, while plastic rollers resist corrosion and reduce noise. The choice depends on load capacity, environment, and operational requirements.
Q: Can damaged return rollers affect conveyor belt performance?
A: Yes, damaged rollers cause belt misalignment, increased friction, and uneven wear. This leads to higher energy consumption, belt damage, and potential unplanned downtime.
-
Trusted Conveyor Solutions from Leading Conveyor Idler Roller ManufacturersNewsJun.27,2025
-
Reliable Return Idler Solutions for Efficient Belt Conveyor SystemsNewsJun.27,2025
-
Precision Conveyor Accessories for Streamlined Material HandlingNewsJun.27,2025
-
High-Quality Belt Conveyor Idler Solutions for Efficient Material HandlingNewsJun.27,2025
-
High-Performance Belt Conveyor Pulleys for Reliable Material HandlingNewsJun.27,2025
-
Enhancing Material Handling EfficiencyNewsJun.27,2025





























