 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu types of conveyor belt rollers
Types of Conveyor Belt Rollers
Conveyor belt systems are integral to many industries, ranging from manufacturing to mining, where they are used to transport materials efficiently. A crucial component of these systems is conveyor belt rollers. These rollers support the belt and facilitate the movement of materials, which can have a significant impact on the system's overall efficiency and productivity. Understanding the different types of conveyor belt rollers can help in selecting the appropriate roller for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance.
1. Idler Rollers
Idler rollers are perhaps the most common type found in conveyor systems. They provide support to the conveyor belt between the drives and loading points. These rollers do not transmit power; instead, they serve to stabilize and evenly distribute the load on the belt. Idler rollers come in various configurations, including flat, rubber-coated, and trough-shaped designs. The choice of idler roller can depend on several factors, including the type of material being transported, the load capacity required, and environmental conditions.
2. Drive Rollers
Drive rollers are essential for propelling the conveyor belt forward. These rollers are equipped with a motor that provides the necessary force to move the belt and the materials it carries. Drive rollers can be found at one end of the conveyor system and are typically designed to create friction with the belt to ensure effective motion. Key factors affecting drive roller performance include the roller's diameter, surface texture, and material composition.
Return rollers are utilized to support the belt on its return trip from the discharge end back to the load point. They play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the belt and preventing sagging, which can lead to inefficient operation and premature wear. Return rollers are generally placed in a straight alignment along the idle side of the conveyor system. Some designs come equipped with rubber coatings to reduce noise and minimize wear on the belt.
types of conveyor belt rollers
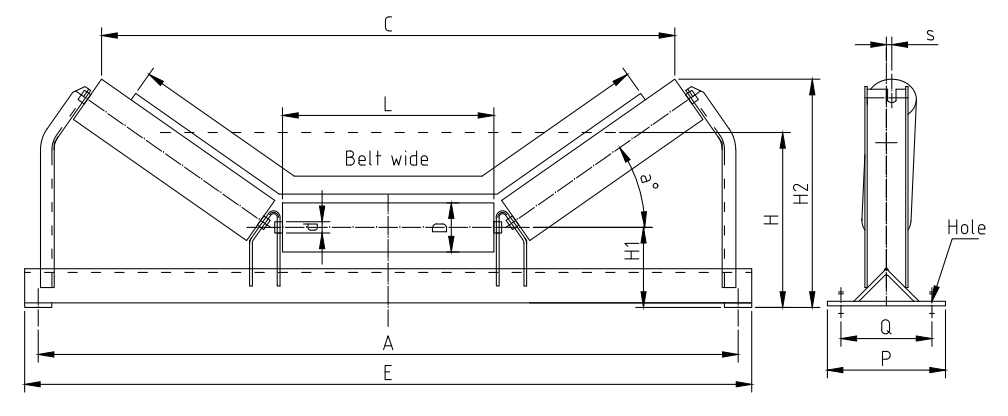
4. Impact Rollers
In scenarios where materials are loaded onto a conveyor belt, impact rollers are utilized to cushion the fall and reduce the risk of damage to both the belt and the rollers themselves. These rollers are often found at the loading zones where heavy materials are transferred onto the belt. They feature a special design that can absorb shock, which helps maintain the conveyor's operational efficiency and extends its lifespan.
5. Washing Rollers
Washing rollers are specialized rollers that play a crucial role in certain manufacturing processes where cleanliness is essential. These rollers are designed to facilitate the cleaning of the conveyor belt while in motion, ensuring that materials do not contaminate the product during transport. They are particularly useful in the food processing industry.
6. Trough Rollers
Trough rollers are designed to hold the conveyor belt in a trough shape, which helps to contain the material and prevent spillage. Troughing (the act of curving the belt) increases load capacity and minimizes material loss, especially for bulk products. Trough rollers are often adjustable, allowing operators to customize the angle based on the specific requirements of the application.
Conclusion
Selecting the right type of conveyor belt roller significantly influences the efficiency, safety, and lifespan of a conveyor system. As industries continue to evolve and demand higher productivity levels, innovative roller designs and materials will play a pivotal role in enhancing conveyor performance. By understanding the various types of conveyor rollers available, businesses can make informed decisions, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. Whether it's an idler, drive, return, or specialty roller, each roller type has its specific function, and recognizing these differences is key to optimizing any conveyor operation.
-
Wing Pulley Conveyor for Conveyor Belt MaintenanceNewsJun.16,2025
-
Self Cleaning Spiral Idler for Conveyor DesignNewsJun.16,2025
-
Pulley Lagging for Conveyor Belt AlignmentNewsJun.16,2025
-
Impact Idlers Used in Belt Conveyor for PerformanceNewsJun.16,2025
-
Ceramic Lagging Conveyor Pulley for Conveyor Belt SystemsNewsJun.16,2025
-
Belt Conveyor Idler for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.16,2025





























