 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu conveyor idler specifications
Understanding Conveyor Idler Specifications Essential Insights for Efficient Material Handling
Conveyor systems are a vital component in various industries, facilitating the smooth movement of materials across different processes. One of the key elements within these systems is the conveyor idler. These components play a crucial role in supporting the conveyor belt, helping to maintain its alignment, and reducing friction as materials are transported. Understanding conveyor idler specifications is critical for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring long-term reliability.
What Are Conveyor Idlers?
Conveyor idlers are cylindrical components that are mounted on frames, typically aligned parallel to the conveyor belt. They serve multiple functions, such as supporting the weight of the belt and its load, guiding the belt and preventing sagging, and minimizing belt wear through friction reduction. Idlers come in various configurations, depending on their application and the type of materials being transported.
Key Specifications
1. Idler Types Idlers can be classified into several types, including flat, trough, and return idlers. Flat idlers are primarily used for light-duty applications, while trough idlers are designed to carry bulk materials and provide better load containment. Return idlers serve the purpose of guiding the belt as it returns to the loading point.
2. Roll Diameter The diameter of the idler roll significantly affects the performance of the conveyor system. Standard diameters range from 4 inches to 8 inches, with larger diameters generally being more effective for heavy loads. A larger diameter reduces the bending stress on the belt and provides better support for the conveyed materials.
conveyor idler specifications
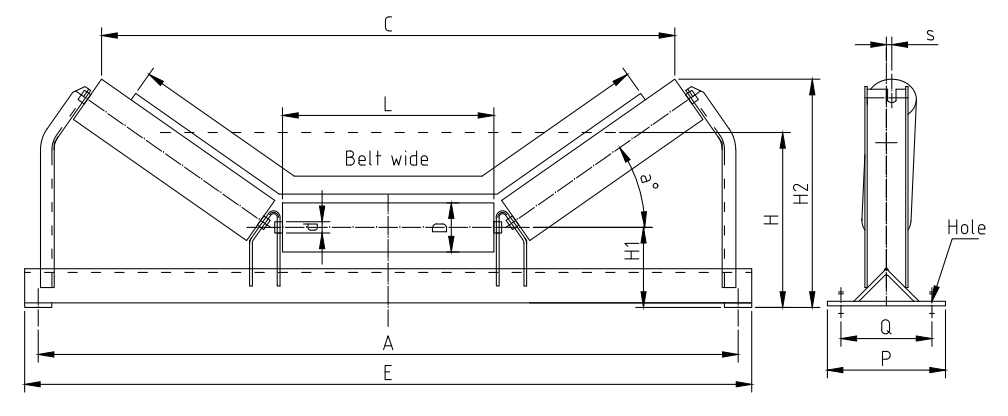
3. Roll Length The width of the idler roll should match the width of the conveyor belt to ensure proper loading and to prevent spillage of materials. Idler lengths typically range from 20 inches to over 60 inches, with longer rolls used for wider belts. Proper selection of roll length is crucial for maintaining belt alignment and preventing uneven wear.
4. Material and Construction Idlers are usually constructed from steel, although plastic and rubber materials may also be used for specific applications. Steel idlers are durable and suitable for heavy loads, while plastic idlers may be better for environments where corrosion is a concern. The construction must ensure strength and resistance to wear and tear under various operating conditions.
5. Bearing Types The bearings used in idlers can be either standard or sealed. Standard bearings require regular maintenance and lubrication, which can be time-consuming. Sealed bearings, on the other hand, are maintenance-free and last longer, making them a popular choice for many applications.
6. Frame and Mounting The frame that supports the idler must be robust enough to handle the loads and stresses exerted on it during operation. Proper mounting of the idler is also critical to ensure that the conveyor belt maintains optimal alignment and tension.
Importance of Specifications
Selecting the right conveyor idler specifications is essential for maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of a conveyor system. Properly configured idlers reduce operational costs by minimizing wear on the belt and decreasing energy consumption. Additionally, understanding the specifications helps in achieving better material flow and reducing downtime for maintenance.
In conclusion, comprehensive knowledge of conveyor idler specifications—including type, roll diameter, roll length, material, bearing type, and mounting—is vital for anyone involved in material handling. By choosing the right idlers tailored to specific operational needs, companies can enhance productivity, minimize costs, and ensure a smooth and reliable material handling process. Making informed decisions about idler specifications is not just an engineering concern; it is a strategic approach to achieving operational excellence in any industrial setting.
-
Wing Pulley Conveyor for Conveyor Belt MaintenanceNewsJun.16,2025
-
Self Cleaning Spiral Idler for Conveyor DesignNewsJun.16,2025
-
Pulley Lagging for Conveyor Belt AlignmentNewsJun.16,2025
-
Impact Idlers Used in Belt Conveyor for PerformanceNewsJun.16,2025
-
Ceramic Lagging Conveyor Pulley for Conveyor Belt SystemsNewsJun.16,2025
-
Belt Conveyor Idler for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.16,2025





























