 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Conveyor Pulley Design and Performance Standards for Efficient Material Handling Systems
Understanding Conveyor Pulley Specifications
Conveyor systems are crucial in various industries, facilitating the seamless movement of materials from one point to another. At the heart of these systems lies the conveyor pulley, a component that plays a pivotal role in the efficient operation of conveyors. Understanding conveyor pulley specifications is essential for manufacturers, engineers, and operators to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Types of Conveyor Pulleys
Conveyor pulleys are typically classified into several types based on their design and application. The primary types include
1. Drive Pulleys These are responsible for transmitting power to the conveyor belt. They usually feature a rugged design to withstand the stresses of constant operation and often come equipped with a lagging surface to enhance grip.
2. Idler Pulleys Idler pulleys support the belt’s tension and shape but do not drive the belt. They are commonly employed in various configurations to maintain belt alignment and minimize sagging.
3. Tail Pulleys Positioned at the end of the conveyor system, tail pulleys facilitate the return side of the belt. They are critical in maintaining tension within the system.
4. Snub Pulleys These pulleys are used to redirect the belt and increase the contact area between the belt and the drive pulley, improving traction and efficiency.
Key Specifications
When selecting a conveyor pulley, several specifications must be considered to ensure compatibility and reliability. Key specifications include
conveyor pulley specification
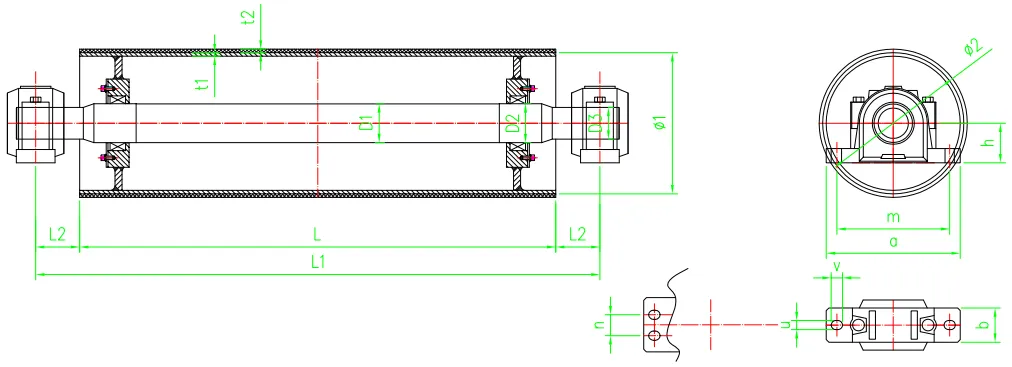
1. Diameter The diameter of the pulley affects the belt's tension and its ability to handle the material load. Larger diameters can reduce belt wear and slippage, while smaller diameters may be necessary for tight spaces.
2. Face Width The face width of the pulley should match the width of the conveyor belt. A proper match ensures that materials are contained effectively on the belt during transport.
3. Material Pulleys are constructed from various materials, including steel, aluminum, and rubber. The choice of material affects durability, weight, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
4. Load Capacity Every pulley is rated for a specific load capacity, which is crucial for ensuring that it can handle the stresses of the materials being transported without failure.
5. Bushing Type The bushing connects the pulley to the shaft. Different types of bushings, including tapered, straight, and locking, provide various levels of engagement and ease of maintenance.
6. Lagging Lagging is often applied to the surface of a drive pulley to increase friction between the pulley and the belt. Available in rubber, ceramic, and other materials, lagging improves traction and extends the life of both the pulley and the conveyor belt.
Maintenance Considerations
Regular maintenance of conveyor pulleys is essential to ensure their longevity and efficient operation. Operators should regularly inspect pulleys for signs of wear, misalignment, and damage. Lubricating bearings and checking for any debris build-up can help prevent unexpected failures.
Implementing proper maintenance schedules and adhering to manufacturer recommendations are critical for maintaining the performance of the entire conveyor system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the specifications of conveyor pulleys is fundamental for optimizing the performance and reliability of conveyor systems. By considering the type of pulley, key specifications, and maintenance practices, operators can significantly enhance productivity and reduce downtime in their operations. With the right knowledge and tailored solutions, businesses can ensure that their conveyor systems operate at peak efficiency, contributing to overall operational success.





























