 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu conveyor belt pulley types
Understanding Conveyor Belt Pulley Types
Conveyor belt systems play a crucial role in various industries, facilitating the efficient movement of materials and products. One of the most essential components of these systems is the conveyor belt pulley. Pulleys are used not only to alter the direction of the belt, but also to provide tension, support the weight of materials, and assist in drive mechanisms. Understanding the different types of conveyor belt pulleys is vital for anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of these systems.
1. Drive Pulley
The drive pulley is the primary component that drives the conveyor belt. It is usually powered by a motor through a series of gears or chains. Drive pulleys are designed to withstand wear and tear from constant use and environmental factors. They come in various materials, including steel, aluminum, and rubber, depending on the application. Properly selecting a drive pulley not only enhances the efficiency of the conveyor system but also prolongs its lifespan.
2. Idler Pulley
Idler pulleys are crucial components that help maintain tension in the conveyor belt. They are positioned along the length of the conveyor system and do not provide any drive power. Instead, they support the weight of the belt and the materials it carries. Idler pulleys come in various designs, including troughing idlers, which have a V-shaped configuration for carrying bulk materials, and flat idlers, which are used for general material handling. The choice of idler pulley affects the belt's performance and longevity, making it essential to choose the right type based on the specific material being transported.
3. Tail Pulley
conveyor belt pulley types
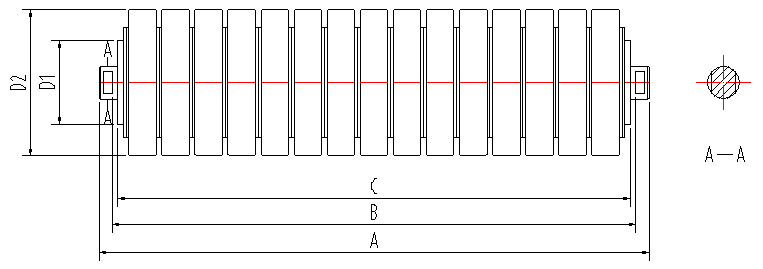
As the name suggests, the tail pulley is located at the end of the conveyor system. Its primary function is to return the belt to the start of the process after the material has been unloaded. Tail pulleys must be robust to handle the weight of the returning belt and any residual material that may cling to it. Many tail pulleys are designed with a crown or taper to facilitate better belt tracking, ensuring that the belt remains aligned throughout its operation.
4. Take-Up Pulley
Take-up pulleys are essential for maintaining the tension of the conveyor belt, especially in systems where the belt may stretch or wear over time. Positioned near the tail end or along the conveyor, these pulleys allow for the adjustment of belt tension. There are two types of take-up pulleys automatic and manual. Automatic take-up systems adjust the tension using a weight mechanism, while manual systems require operators to adjust the tension manually. Proper tensioning is vital to prevent slippage, reduce wear, and ensure efficient operation.
5. Snub Pulley
Snub pulleys are used to change the direction the conveyor belt takes. They function by providing additional contact points along the belt's path, which can improve tracking and minimize belt wear. Snub pulleys are often incorporated into systems that require sharp turns or changes in elevation. While they are not as critical as drive or idler pulleys, their role in maintaining belt alignment and longevity should not be underestimated.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of conveyor belt pulleys is essential for anyone involved in the design, maintenance, or operation of conveyor systems. Each type of pulley—drive, idler, tail, take-up, and snub—serves a unique function that contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the conveyor system. By selecting the right pulley for specific applications, operators can ensure optimal performance, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Whether in manufacturing, mining, or logistics, having a thorough knowledge of conveyor belt pulley types is a vital skill that can drive success in material handling operations.
-
Taper Centering Idler Set for Conveyor SystemsNewsJun.25,2025
-
Small Idler Rollers for Industrial ConveyorsNewsJun.25,2025
-
Guide Training Idler Set for Conveyor MaintenanceNewsJun.25,2025
-
Friction Offset Idler Set for Industrial UseNewsJun.25,2025
-
Double-Center-Roller Idler AlignmentNewsJun.25,2025
-
Channel Inset Impact Troughing Idler Set for Heavy LoadsNewsJun.25,2025





























