 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu Various Types of Conveyor Belt Pulleys and Their Applications in Industry
Types of Conveyor Belt Pulleys
Conveyor belts are an essential component in material handling systems, playing a key role in transporting goods from one location to another efficiently. Pulleys are integral parts of these systems, enabling the smooth operation of conveyor belts. Understanding the different types of conveyor belt pulleys is crucial for selecting the right components for an efficient conveyor system. In this article, we will explore the various types of conveyor belt pulleys, their functions, and applications.
1. Drive Pulleys
Drive pulleys, also known as head pulleys, are responsible for imparting motion to the conveyor belt. Positioned at the end of the conveyor system, they are connected to a motor that turns the pulley, driving the belt forward. The design of a drive pulley is typically larger to provide adequate belt traction and support the weight of the materials being transported. Additionally, drive pulleys can come with various surface materials, such as rubber or grooved surfaces, to enhance grip and reduce slippage during operation.
2. Idler Pulleys
Idler pulleys are used to support the conveyor belt as it moves around the system. Positioned along the conveyor's length, these pulleys help maintain belt tension and alignment. They do not drive the belt but are critical for ensuring smooth and stable operation. Idler pulleys can be designed in different configurations, including plain, grooved, and wings, depending on the specific requirements of the conveyor system they are being used in.
3. Tail Pulleys
Tail pulleys are located at the opposite end of the drive pulleys and play a vital role in guiding the conveyor belt back to its starting position. They help in tensioning the belt and returning it to the drive pulley. Tail pulleys are generally designed to withstand the dynamic forces of the belt and the materials being transported. Similar to drive pulleys, tail pulleys can vary in size and design to suit the particular conveyor system.
types of conveyor belt pulleys
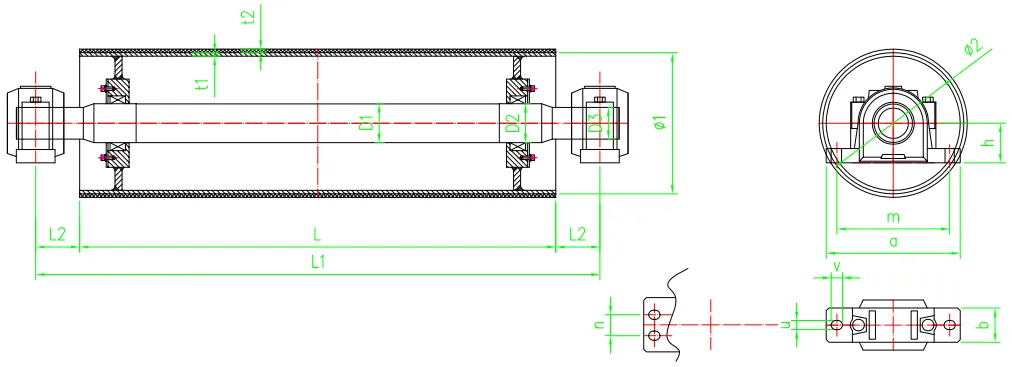
4. Snub Pulleys
Snub pulleys are used to increase the friction between the drive pulley and the conveyor belt, thereby enhancing the belt's traction and improving its grip. This is particularly useful in systems that require a high level of tension or where the angle of the belt changes frequently. Snub pulleys are often positioned beneath the drive pulley and can be a valuable addition for increasing efficiency in a conveyor system.
5. Bend Pulleys
Bend pulleys are employed to change the direction of the conveyor belt, which is crucial in systems with specific layout constraints. These pulleys can redirect the belt at various angles, allowing for more complex conveyor designs. Bend pulleys can help in maximizing the space available while ensuring the smooth flow of materials along the conveyor path.
6. Take-Up Pulleys
Take-up pulleys are essential for maintaining proper tension in a conveyor belt system. Located at the non-drive end of the conveyor, they allow for adjustment of the belt's tension during operation. This is particularly important as belts can stretch over time or due to load changes. Having an efficient take-up mechanism helps prolong the life of the conveyor belt and ensures reliable performance.
Conclusion
In summary, conveyor belt pulleys are vital components that contribute significantly to the efficiency and effectiveness of conveyor systems. Understanding the various types of pulleys—drive, idler, tail, snub, bend, and take-up—can help engineers and operators select the right components for their specific applications. By ensuring the right combination of pulley types, organizations can not only improve their material handling processes but also enhance system longevity and reliability.
-
Revolutionizing Conveyor Reliability with Advanced Rubber Lagging PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Powering Precision and Durability with Expert Manufacturers of Conveyor ComponentsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Optimizing Conveyor Systems with Advanced Conveyor AccessoriesNewsJul.22,2025
-
Maximize Conveyor Efficiency with Quality Conveyor Idler PulleysNewsJul.22,2025
-
Future-Proof Your Conveyor System with High-Performance Polyurethane RollerNewsJul.22,2025
-
Driving Efficiency Forward with Quality Idlers and RollersNewsJul.22,2025





























